In order to understand what HR professionalism is we first have to break down what it means to be a professional. The term professional could be an individual who is a qualified member of a professional body, someone who continuously updates their knowledge, is competent, and uses their skills in practice. Professionalism could be interpreted as the use of specialist knowledge necessary to perform a particular type of work or role. Professionals are associated with increased training, the development of professional knowledge standards, and a requirement to update this knowledge.
One way the CIPD (The Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development) measures professionalism is through their code of conduct which can be broken down into 4 sections as shown below:
- Professional Competence and Behaviour
- Ethical Standards and Integrity
- Representative of the Profession
- Stewardship.
These codes of conduct apply to everyone who is registered with the CIPD regardless of size, sector, or specialism. These particular areas help in maintaining and being an effective and efficient HR professional.
Being an Effective and Efficient HR Professional
To be effective and efficient as an HR professional there are many skills that need to be learned and developed. The below list outlines some of the key skills required:
- Effective time-keeping skills
- Project management skills being
- Analytical and critical thinking
- Good communication skills
- Ability to build and manage relationships.
An effective technique for HR professionals is to use an “outside-in” approach where business trends are identified by looking at competitors or other businesses and seeing how they can be utilized internally. Having the company’s priorities in mind is key, as well as being able to give a good service to your customers. HR should look at both individual abilities as well as organizational capabilities in order to maximize their outputs. HR should look at achieving sustainable and integrated solutions rather than isolated activities like staffing and compensation programs. Past HR practices should be developed and adapted to become more efficient and effective in current practices. HR includes an administrative function as well as strategic meaning as you have to be able to manage not only the day-to-day administrative processes but also the long-term strategic practices.
The Thinking Performer
The Thinking performer is one of four different types of people within an organization. These four types of people are:
- The Lifetime Liability – the employee who neither performs nor thinks.
- The Wish-List Dreamer – the thinking non-performer who if he has ideas, keeps them to themselves.
- Automated Bureaucrat – the non-thinking performer who does what he’s told and no more.
- Thinking Performer – the ‘strategic activist’ employee who adds value through continuous challenge and self-imposed improvement goals.
An HR professional should always aim to be a Thinking Performer who is proactive in driving their business forward whilst adhering to organizational rules and regulations. The status quo should be challenged in order to improve current practices and find the most effective solutions. As an HR professional, you should understand your customers in order to develop services that meet their needs and therefore meet your organizational goals. Feedback via word of mouth, mystery shoppers, and surveys should also be sought as this is a key component of understanding your customers.
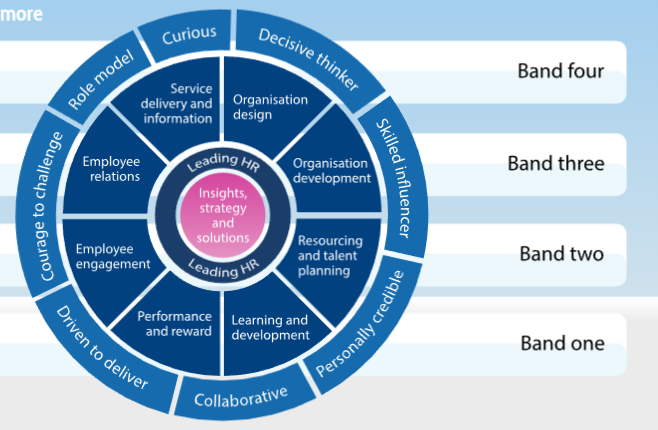
CIPD Professional Map
To understand how professionalism can be conveyed in an HR role we can refer to the CIPD professionalism map below: “The 2013 Map defines the building blocks of effective people management practice … that underpin good practice regardless of specialism. It’s also flexible, so you can choose what to focus on depending on your area of work, the level of accountability you have in your role, and your career development ambitions.” (CIPD (n.d), 2013).
The CIPD map above is broken down into the following sections:
- Insights, strategy, and solutions – This is to help establish an understanding of the organization and use these insights to tailor strategy and solutions to meet the organization not only short-term goals but also in the long term.
- Leading HR – Lead the way for an Hr professional by acting as a role model, by helping further your contributions either in Hr or across other areas of the business as well as developing and measuring others across the organization.
- Organization design – Ensure the organization is designed to deliver maximum impact both for the present goals and the future.
- Organization development – This can be done by Identifying organizational and individual capability and using this to help align strategy, people, and processes to optimize effectiveness and achieve organization goals.
- Resourcing and talent planning – Ensure that the organization has the right resource, capabilities, and talent as well as an active effective strategy to achieve ambitions now and in the future.
- Learning and development – By working on your own as well as organizational capability and knowledge to meet current requirements, and create a learning culture to embed capability development.
- Performance and reward – Help create and maintain a high-achieving culture by delivering programs that reward and recognize key employee capabilities, skills, behaviors, experience, and performance, and ensure that reward systems are fair and cost-effective.
- Employee engagement – Work to strengthen the relationships between employees’ colleagues and their work so that they make a greater contribution toward organizational objectives.
- Employee relations – Ensure that the relationship between the organization and its employees are managed appropriately effectively and efficiently underpinned by organization standard, policies, and ultimately by relevant law.
- Service delivery and information – Ensure that you have customer-focused HR delivery across the entire service and implement processes and project management to enable effective and cost-efficient HR service delivery as well as analyze its utilization.
Analyzing the 4 bands of professional competence we can understand that these bands represent the stages every HR Professional should take in his career and the contribution or value the HR professional brings to the organization (as a whole, through teams, processes or individuals). These 4 bands reflect both competencies/behaviors and professional areas. The bands the contribution the HR Professional should have in each of the following key areas:
Moving towards the professional areas, we can notice that there are 2 core areas that underpin all the HR Map together. They are Insights, Strategy, Solutions, and Leading HR and the reason why they are being central is that they are applicable to all HR professionals, regardless of role(specialist, generalist, L&D), location(worldwide), or stage of career(from band 1 to 4), whether inside organizations (internal) or working with them (contactors or consultants).
The banding system allows you to match yourself to your current band of competence and see what is needed to move up in the bands and see where you are lacking in your current band to improve.
Four Concentric Circles of HR Professionalism
The four concentric circles help show you where HR professionalism can be slotted into, these are:
- Managing self
- Managing in groups/teams
- Managing upwards
- Managing across the organization
1. Managing self refers to the ability to manage your own skills knowledge and behaviors by keeping them up to date. Without these skills, your relationships with colleagues or other individuals may not be as effective.
2. Managing in groups or teams could involve working with other HR professionals or other colleagues to help solve organizational problems or working with other key stakeholders.
3. Managing upwards, as an HR professionals, we are required to work closely with our managers and senior professionals within the organization. Without this, any organization’s strategies or plans will struggle to be implemented across the wider organization.
4. The last circle of professionalism refers to ‘managing across the organization. Once a plan has been created it is then up to the HR professionals to set these plans into motion across their organizations.
Providing Excellent Service
In order to be successful in HR one key element is to make sure your customers are getting what they need. This could be by replying to queries in a timely manner, being able to be flexible with customers, and expanding your knowledge to help give customers what they want. Friendliness is also key in HR as you have to be someone who your customers want to approach for any HR-related queries. To provide a high-quality service to customers HR professionals should give transparent and accurate information to their customers. While implementing any communications or solutions it is necessary to comply with the policies and procedures set out within the HR role.